|
||||
|
Creating
a Custom Look and Feel
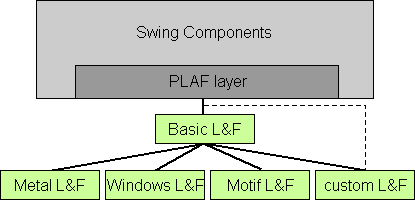
One of SAP AG's software products is a Sales Configuration Engine, or SCE, which enables manufacturers to configure various kinds of products and materials. To do that job, the SCE engine uses modelled data imported from another software system called R/3. (R/3 is the leading software product in the field of enterprise resource planning, which deals, among other things, with Y2K compliance by computer systems.) SAP developed the Sales Configuration Engine using the JavaTM programming language and the Swing GUI component set. The SCE comes with different APIs, as well as with JavaBeanTM components that developers can use to integrate the SCE into their products. There is also a standard user interface, which uses the APIs and the beans to provide a generic configuration application. Not long ago, SAP launched an effort to create a better user interface for the R/3 environment, hopefully with a new look and feel (L&F) that would help promote an updated corporate identity at the UI level. Frog Design, a company that designs professional user interfaces, was commissioned to assist SAP in creating an overall corporate look and feel for SAP, which is summarized in the slogan "Enjoy SAP." Obviously, the company's corporate identity does not stop at R/3. SAP produces several external applications -- including the SCE -- that interact in one way or another with R/3, but are stand-alone applications. To create a corporate look and feel that works at all levels, all these applications will also have to be equipped with features that support the new "Enjoy SAP" guidelines. Because SAP developed the SCE's user interface using Swing, it was only natural to use Swing's pluggable look-and-feel architecture to create a new look and feel for the SCE that would match the overall new look and feel being incorporated into the rest of the company's product line. So far, the new look and feel that has been created for the SCE is not a full-blown implementation of the look and feel being developed for the company's "Enjoy SAP" theme. Since the SCE had a major release coming up, we decided to implement our own interim version of the "Enjoy SAP" and call it the "SCE look and feel." A different team at SAP is currently working on what will eventually become the official Swing implementation of the "Enjoy SAP" look and feel. Because the look and feel architecture of Swing is "pluggable," these two parallel efforts will not interfere with each other. When the time comes, it will be easy to replace our interim "SCE look and feel" with the official implementation of the "Enjoy SAP" look and feel when the final and official version becomes available. Swing's Pluggable L&F ArchitectureAs longtime readers of The Swing Connection know, Swing is a lightweight component architecture. One of the of the most important features of Swing's lightweight component architecture is that the use of Swing requires the creation of almost no GUI component peers at the operating-system level. That's because Swing is responsible for handling the rendering and the interactions of its components. When you create a Swing component, it is actually the Java VM that draws the component at a specified position on the screen. That's what makes Swing's pluggable look and feel (PLAF) architecture possible. When a particular look and feel is plugged in, a specific paint method is called, and that paint method then draws the component in the appropriate way for the specified look and feel. Although all this may sound somewhat complicated, what it all boils down to is that it's simply no longer a big deal to plug different look and feel implementations into an application. With Swing's pluggable-L&F architecture, you can easily equip any application with Swing's Java (formerly called Metal) look and feel -- or, if you wish, you can use the Windows L&F, the Motif L&F, or whatever prepackaged or custom L&F you prefer. To help you choose a look-and-feel, Swing comes with an assortment of prepacked L&Fs that are subclassed from a basic look-and-feel implementation called the BasicLookAndFeel. The BasicLookAndFeel provides a lot of infrastructure that can also be used by other look and feels -- but a new custom look-and-feel does not necessarily have to subclass the BasicLookAndFeel. In fact, Swing provides many possibilities for customizing a look-and-feel. Some of them are shown in the following diagram.
Figure
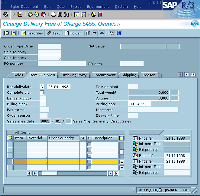
1 The 'Enjoy SAP' L&FFrog Design and SAP created an extensive specification of how the new "Enjoy SAP" look and feel is supposed to look and behave. This specification contains colors, fonts, and descriptions of geometry and behavior. It also describes certain effects that are part of this look and feel. These effects include HSB shifting, shading and transparency based on a color model called HSB. (The interim SCE L&F only implements the HSB shifting effect). The HSB color model does not specify values for red, green and blue, as the RGB color model does. Instead, it defines a color through its hue (its base value on the color circle), its saturation, and its brightness. HSB shifting is particularly useful in creating GUI components, because it allows the designer to alter the standard palette by shifting the hue and saturation values. In that way, the designer can change the palette without losing the distinctiveness of the different colors. Figure 2 shows an example of what an application might one day look like using the "Enjoy SAP" look and feel being developed by SAP AG.
Starting the ProjectWhen we started working on the SCE L&F project, our initial objective was to create a completely separate new look and feel by subclassing it directly from Swing's BasicLookAndFeel. That seemed like a good way to create a look-and-feel framework quite fast. We figured we could take all the sources of the Metal look and feel from the javax.swing.plaf.metal package, copy them to a new package, and then rename everything that included the word "Metal" to a new custom name. Then we could start to modify the code so it would fit our spec. We eventually decided against this approach because we discovered it would result in much more code than we wanted to maintain. Also, it was not quite clear in the beginning which components would be modified and which ones would not be. So our final approach was to subclass the existing look and feel of of the Java ("Metal") look and feel. The geometry and the behavior of the components would then be inherited, and we could make changes where necessary.
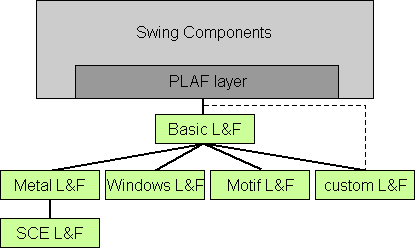
Figure
3 When you start working on customizing a look and feel, you immediately get to the LookAndFeel.java file, which is the heart of the PLAF architecture. In our case, we created a look and feel named SceLookAndFeel.java, which was a subclass of MetalLookAndFeel.java. MetalLookAndFeel, as you may know, is itself a subclass of the abstract class LookAndFeel. Our own SceLookAndFeel class contains all kinds of information about our specific SCE L&F. It maps the L&F-specific user interfaces to specific components (for instance, which class is responsible for painting a button), specifies system defaults and component defaults (for example,. what is the selection color in a table), and also contains color and font specific information (such as which colors and fonts are available). In the case of the Metal L&F, information about color themes is provided as well. This mechanism allowed us to plug different color and font themes into the Metal L&F without changing the geometrie and behaviour of a component. For the SCE L&F, the theme mechanism was disabled, making is no longer possible to plug in a theme into the SCE L&F. The first thing we added to the SceLookAndFeel
class was an "Enjoy SAP"-specific color palette of 256
colors. All previous color
references were then changed to reference the new palette. The mechanism
for the hue-shifting and saturation-shifting was implemented in
the SceLookAndFeel class as well.
In this way, the mechanism directly altered the palette. (When modifying
the LookAndFeel class one has
to keep in mind that existing property names are being reused. The
properties (or: defaults) are kept in a hashtable which maps a color,
font, text, border, etc. resource to a specific key. The resource
is then retrieved through the UIManager
class, by specifying the hashtable key. New properties can be defined
as well, so that your custom drawing code can make use of it, but
existing properties should not be renamed and used for the same
purpose. The first components we modified were buttons; we provided new implementations for both the JButton and JToggleButton components. Figure 4 shows the difference between a JButton in Metal L&F and in SCE L&F:
Figure 4 A Metal button and an SCE button. To implement our new buttons, we created a pair of classes named SceButtonUI and SceToggleButtonUI. We knew that in Swing, new UI subclasses must overwrite the createUI() method if they are to return a correct L&F-specific instance for createUI(). Then the drawing code can be manipulated directly by overwriting the appropriate methods. To create our buttons, we overrode the paintButtonPressed(), paintText() and update() methods because the background, the font and the border of the buttons needed to be changed. Our drawing code made heavy use of the properties that were set in the SceLookAndFeel class. To use the new UI classes, we had to add them to the list of custom UIs in SceLookAndFeel.initClassDefaults(). That way, we made sure that the new UI was properly instantiated and used by the UIManager class. protected void initClassDefaults(UIDefaults table) {
super.initClassDefaults(table);
String ScePackageName = "com.sap.sce.front.plaf.";
Object[] uiDefaults = {
"ButtonUI", ScePackageName + "SceButtonUI",
"MenuUI", ScePackageName + "SceMenuUI",
"ProgressBarUI", ScePackageName + "SceProgressBarUI",
"ScrollBarUI", ScePackageName + "SceScrollBarUI",
"SplitPaneUI", ScePackageName + "SceSplitPaneUI",
"TabbedPaneUI", ScePackageName + "SceTabbedPaneUI",
"TableHeaderUI", ScePackageName + "SceTableHeaderUI",
"ToggleButtonUI", ScePackageName + "SceToggleButtonUI",
"ToolBarUI", ScePackageName + "SceToolBarUI",
};
table.putDefaults(uiDefaults);
}
In the same way, we created the other UIs for specific components. Most of our work during this project involved adjusting all the colors in the SceLookAndFeel class and making changes to the utility classes SceBorders.java, SceUtils.java and SceIconFactory.java, which are all directly subclassed from the similar classes in the Metal L&F. Creating the custom UIs was basically a matter of overwriting the specific methods from the superclass and making custom changes. When we started subclassing the Java look and feel, it turned out that the Java L&F could not be subclassed as easily as we had expected. This was because some classes, member variables and methods in the Metal UIs are private or "package private," and thus cannot be accessed in subclasses from a different package. Consequently, the original members or methods must be duplicated in the subclass. That way, quite a bit of code may gets generated, although very little gets changed on the visual end. To our knowledge, the Swing team is already aware of many of the protection issues at work here and is aware of the need to review and perhaps modify them. We also had to look at which components would be implemented in the new SCE L&F and which would not be. Because of the introduction of a new color palette and some changes with the fonts, almost all components had already inherited changes, because all known properties in the SceLookAndFeel class were now referring to the new palette. That meant that all the original components from the Java L&F already appeared in different colors. The UI implementations were now needed to provide other specific notions. For example, the SceTabbedPaneUI class is a subclass of MetalTabbedPaneUI, and as such has the same UI (except the colors and fonts). But we also wanted the text on the active tab to appear in a bold font, while all the other texts appeared in a normal font. Also, we wanted the focus border to be removed. So some of the methods in the original MetalTabbedPaneUI had to be overwritten in the SceTabbedPaneUI class in order to provide this functionality. In the current implementation of the SCE L&F the following changes have been made to the UI:
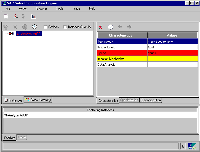
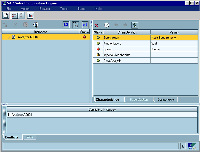
Finally, the finished compilation of the SCE L&F was wrapped into a JAR file and made publicly available to other groups at SAP. As it turned out, there were other groups which were in need of a fast approximation of the new "Enjoy SAP" look and feel, just as we had been. So the SCE L&F was also used for other projects, not just for the SCE. Basically, all you have to do to take full advantage of the new look and feel is make a call to UIManager.setLookAndFeel("com.sap.sce.front.plaf.SceLookAndFeel"). The only problem we encountered during our work on the project occurred because JDKTM 1.2 is currently unable to load custom look-and-feels from the CLASSPATH, so look-and-feel classes must be placed on the BOOTCLASSPATH. This is a bug in JDK 1.2 which Sun is aware of, and which will get fixed in the upcoming JDK 1.2.2 release. In all other respects, our new SCE L&F runs smoothly on the JDK 1.1.x, JDK 1.2 and Microsoft VM. Now What Does It Look Like?Figures 5, 6, and 7 show how our new SCE Look and Feel affects the SCE application. Figure 5 shows what the SCE user interface looked like in the previous release. Figure 6 shows the same application with the new SCE Look and Feel. There are a few functional modifications as well, but their effect to the UI is minor. Figure 7 shows the same application with a hue- and saturation-shifted palette. Figure
5 Figure
6 Figure
7 ConclusionBy the time we finished creating our new L&F, our experience had shown us that Swing is a great architecture on which to base a pluggable look-and-feel. We also found out that with Swing, you can achieve a relatively unique effect by just doing a little bit of work. In the end, your application gets a new and unique makeover at a very small cost. The implementation of our SCE L&F in its current version took one developer about 2.5 weeks to finish. We also learned that when you design a new look-and-feel using Swing, the possibility of introducing new UI-related bugs is relatively low, since the new L&F is based on one that already exists. Modifications happen locally and can be isolated easily. Our new SCE L&F seems to have been readily accepted at SAP, since it has already adopted by other projects within in the company. So our efforts have helped to close the gap between now and the time when the official Swing-based implementation of the "Enjoy SAP" look and feel will be available. Several books have documented the creation of a custom L&F using Swing. Books I would recommend at this point for their coverage of the topic include Graphic Java, Mastering the JFC, Volume 2 by David Geary and JFC Unleashed by Michael Foley and Mark McCulley. Thanks, David, Michael and Mark for those little helpers that make the Swing developers every day job a bit easier. Most important, I would also like to thank the Swing team for their continuing help and their patience in answering all the little questions I had during this project. You guys are doing a great and outstanding job. Keep up the good work! |
.gif)